Cybersecurity is a topic that often sounds more complex — and more frightening — than it needs to be. In recent years, EV chargers have joined the list of “connected devices,” which means cybersecurity questions now appear in tenders, sales discussions, and boardroom decisions.
This article explains cybersecurity in EV charging in a clear and realistic way. It is written for buyers, site owners, and sales teams who need to understand the topic well enough to make good decisions — without technical overload or fear-based thinking.
What cybersecurity means in simple terms
Cybersecurity is about protecting systems from unauthorized access, misuse, or disruption.
In practice, this means:
- Making sure only authorized people and systems can access a device or service
- Protecting communication between devices and servers
- Reducing the risk of data manipulation, service interruption, or misuse
Cybersecurity is not about achieving “zero risk.” That does not exist in any connected system. It is about managing risk responsibly and proportionally.

Why EV chargers are considered connected devices
An EV charger is no longer just a power outlet. Most modern chargers are connected in some way to:
- A backend system for monitoring and billing
- A local network
- The internet (directly or indirectly)
Because of this connectivity, EV chargers fall into the same broad category as other networked devices such as routers, smart meters, or industrial controllers.
This does not automatically make them dangerous. It simply means they must be designed and operated with basic security principles in mind.
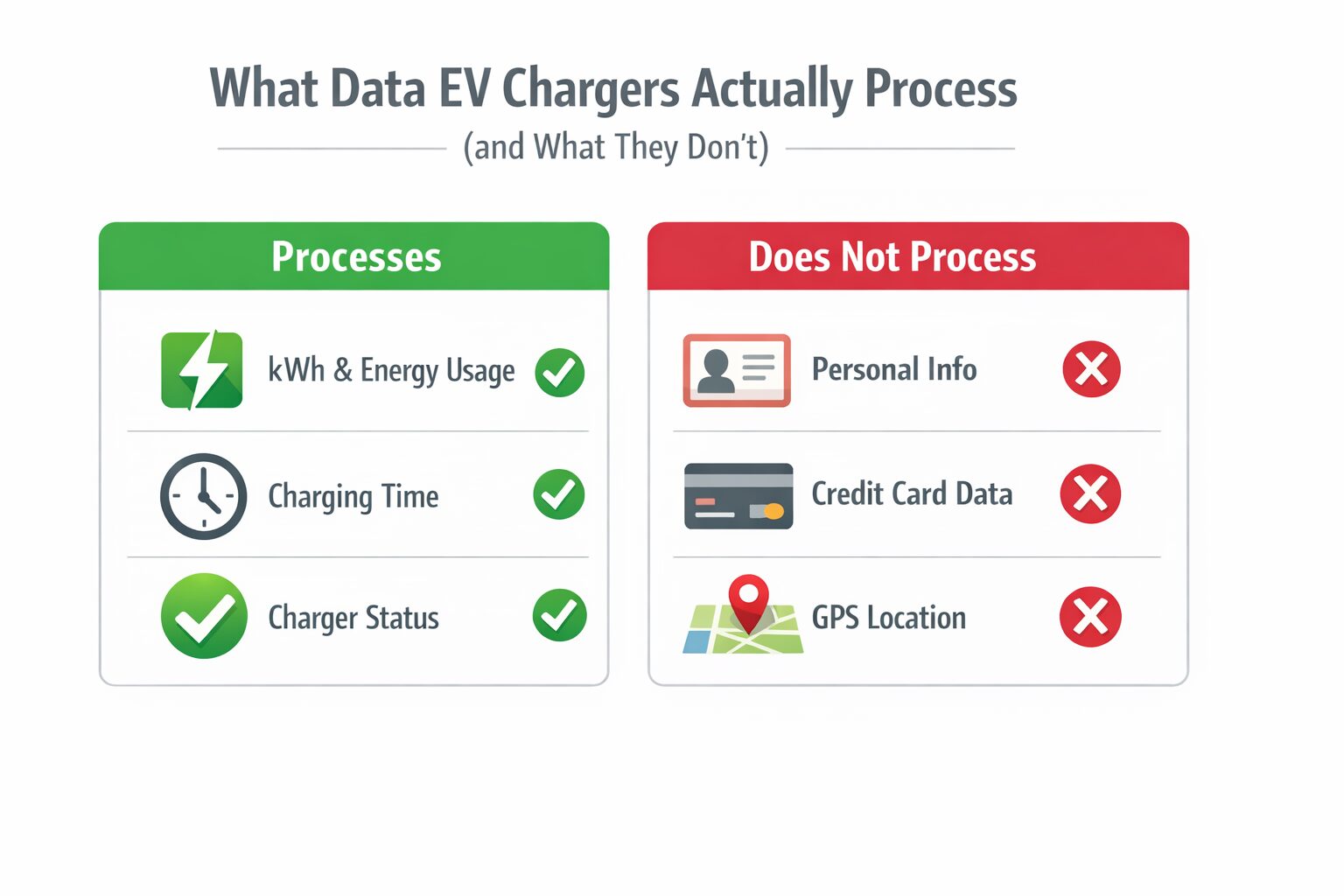
What data EV chargers actually process (and what they don’t)
One of the biggest misunderstandings around EV charger cybersecurity is the type of data involved.
What EV chargers typically process
- Charger ID and location
- Charging session start and stop times
- Energy delivered (kWh)
- Status information (available, charging, fault)
- User identifiers such as RFID card IDs or app-based session IDs
What EV chargers do not process
- Credit card numbers (handled by payment providers)
- Personal identity data like names, addresses, or ID numbers
- Vehicle driving data or GPS tracking
- Private data stored inside the car
In most systems, EV chargers handle operational and billing-related data — not sensitive personal data. This significantly limits the potential impact of a cybersecurity incident.
Typical cybersecurity risks in EV charging infrastructure
Like any connected system, EV charging infrastructure has potential risks. The key is understanding which risks are realistic and which are often overstated.
Common realistic risks
- Unauthorized access to charger configuration
- Disruption of communication between charger and backend
- Temporary service unavailability
- Misuse of poorly protected local networks
Less realistic fears
- Mass vehicle hacking via chargers
- Chargers spying on users
- Chargers controlling vehicles beyond charging functions
EV chargers are designed with very limited control over the vehicle. Their role is energy delivery and session management — not vehicle operation.
Device security, network security, and backend security
Cybersecurity in EV charging is not one single thing. It consists of several layers.
Device security (the charger itself)
This includes:
- Secure firmware
- Controlled access to configuration interfaces
- Protection against unauthorized software changes
A charger should not accept unknown firmware or allow unrestricted access to its internal settings.
Network security
This refers to how the charger is connected:
- Ethernet, mobile network (4G/5G), or Wi-Fi
- Firewalls and network segmentation
- Secure communication channels
Many risks attributed to chargers actually come from weak local networks, not the charger itself.
Backend security
The backend system manages:
- User access
- Billing
- Data storage
- Remote control and monitoring
In most cases, the backend is the most critical security component. A professionally managed backend with proper access control and monitoring is essential.
The role of OCPP and backend communication
OCPP (Open Charge Point Protocol) is the standard communication protocol used between EV chargers and backend systems.
Why OCPP matters for security
- It defines how data is exchanged
- It supports encrypted communication (TLS)
- It allows authentication between charger and backend
OCPP itself is not a security risk. Like any protocol, it must be implemented correctly and used with proper encryption and access control.
Security issues usually arise from:
- Misconfigured backends
- Weak credentials
- Poor network setup
Not from OCPP as a concept.

Responsibilities: who is responsible for what?
Cybersecurity is a shared responsibility.
Manufacturers are responsible for
- Secure charger design
- Firmware integrity
- Secure update mechanisms
- Basic access control
Operators and backend providers are responsible for
- Secure backend infrastructure
- User access management
- Monitoring and logging
- Secure communication channels
Site owners and buyers are responsible for
- Choosing professional solutions
- Maintaining network hygiene
- Keeping systems updated
- Following basic operational best practices
Cybersecurity failures usually happen when responsibilities are unclear or ignored — not because a charger is inherently insecure.
What buyers and site owners should realistically care about
Buyers do not need to become cybersecurity experts. A few practical questions are usually enough:
- Is communication encrypted?
- Is firmware controlled and updateable?
- Is the backend professionally managed?
- Are access rights clearly defined?
- Is the charger isolated from critical internal networks?
If these basics are covered, the cybersecurity risk is typically well within acceptable limits for EV charging infrastructure.
Common myths vs reality
Myth: EV chargers are high-risk hacking targets
Reality: EV chargers are low-value targets compared to financial systems, telecom networks, or cloud services.
Myth: A charger can easily hack a vehicle
Reality: Chargers have very limited interaction with the vehicle, focused on charging control only.
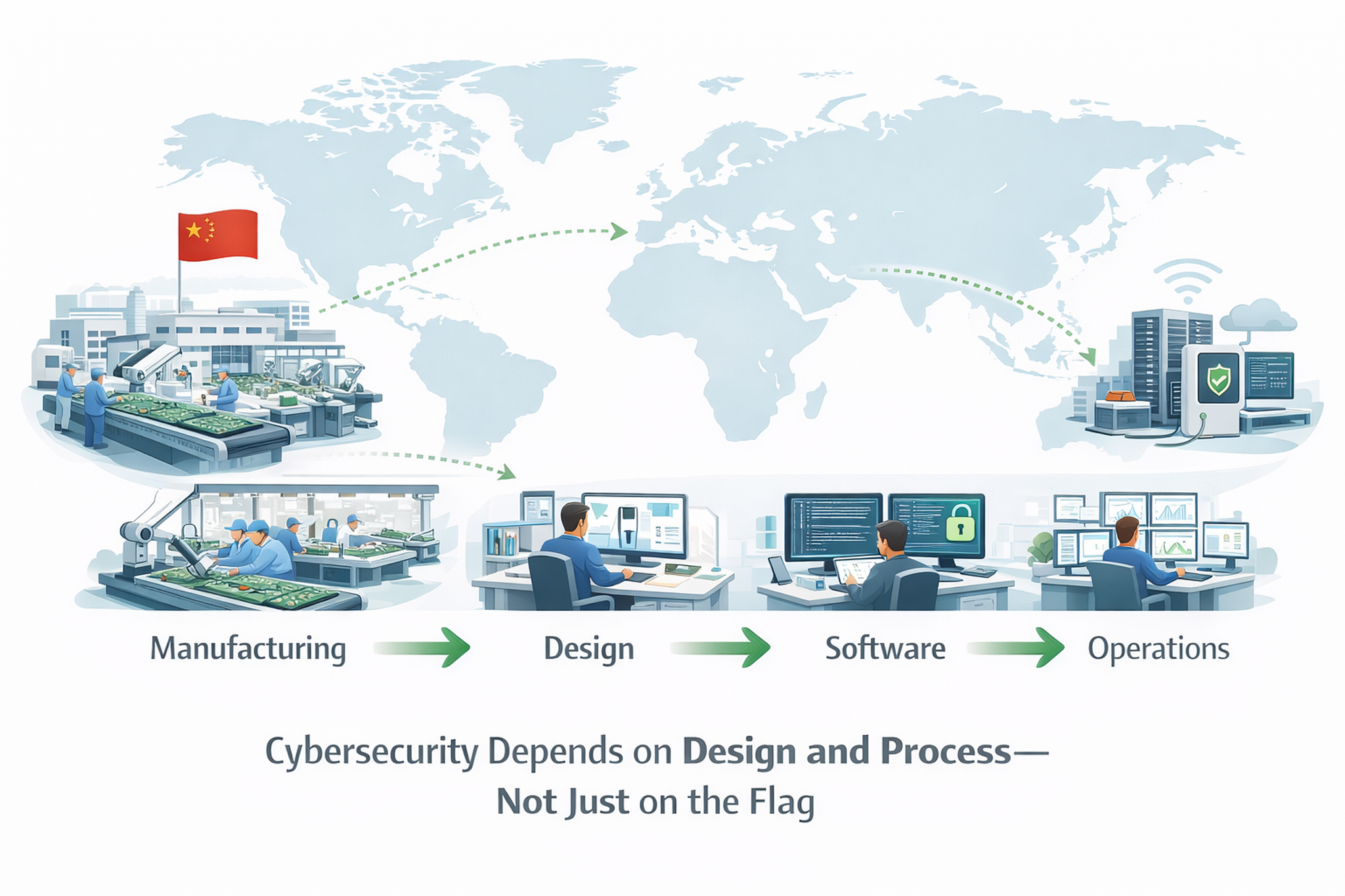
Myth: “Made in China” means insecure
Reality: Country of manufacturing does not determine cybersecurity.
Most electronic devices worldwide are manufactured in China — including routers, smartphones, laptops, and industrial equipment. Security depends on:
- Design
- Firmware control
- Update processes
- Operational practices
A well-designed charger manufactured in China can be more secure than a poorly designed charger manufactured elsewhere.
Cybersecurity is about engineering and process, not geography.
Best practices without technical complexity
For buyers, operators, and sales teams, the following best practices are usually sufficient:
- Use encrypted communication (TLS)
- Avoid default passwords
- Separate charger networks from internal business systems
- Keep firmware and backend software up to date
- Work with reputable backend providers
- Document access rights and responsibilities
These steps address the majority of real-world cybersecurity risks in EV charging.
Conclusion: a balanced view on EV charging cybersecurity
Cybersecurity in EV charging is important — but it does not need to be dramatic or fear-driven.
EV chargers are operational devices that handle limited data and perform a specific function. When designed, installed, and operated professionally, they do not represent a significant cybersecurity threat.
Understanding the basics helps buyers make confident decisions, helps sales teams explain the topic clearly, and builds trust in modern EV charging infrastructure.
Cybersecurity is not about perfection. It is about responsibility, clarity, and realistic risk management.